
Gum surgery is a procedure performed to treat various gum-related issues, such as gum recession, gum disease, or to prepare for restorative treatments like dental implants. The goal of gum surgery is to restore gum health, improve the appearance of your smile, and prevent further damage to your teeth and gums.
There are different types of gum surgery, including soft tissue grafting, pocket reduction, and crown lengthening, each designed to address specific concerns. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, and recovery time can vary depending on the type of surgery.
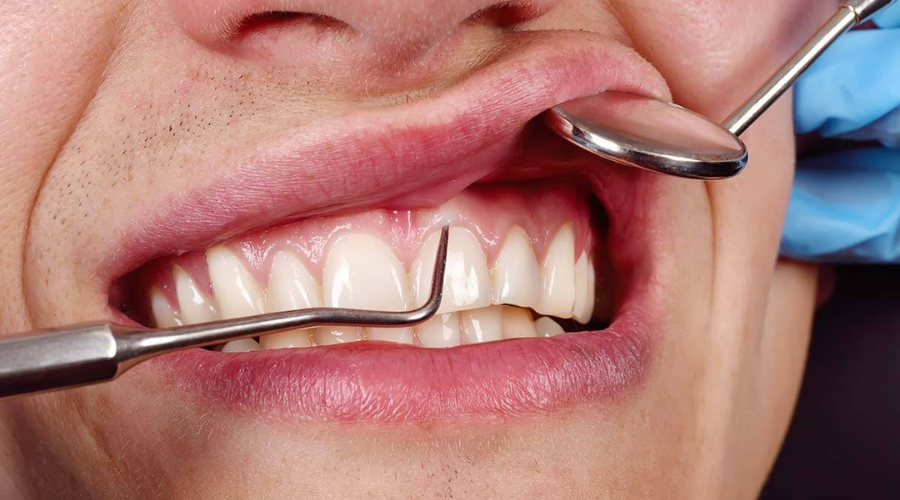
The procedure begins with a thorough examination of the gums to assess the severity of gum disease. The dentist or periodontist performs a deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria from beneath the gum line. This helps reduce inflammation and prepares the gums for surgery if needed.
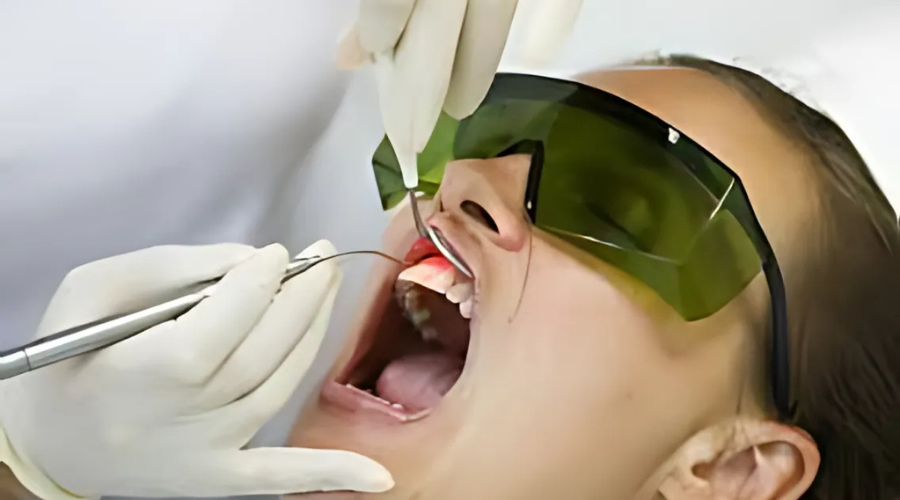
If deep cleaning alone isn’t enough, a surgical procedure such as flap surgery or gum grafting is performed. In flap surgery, the gums are lifted to remove bacteria and tartar from deep pockets, then sutured back for proper healing. If gum recession is severe, a gum graft may be done, where tissue from another part of the mouth (or a donor source) is used to rebuild lost gum tissue.
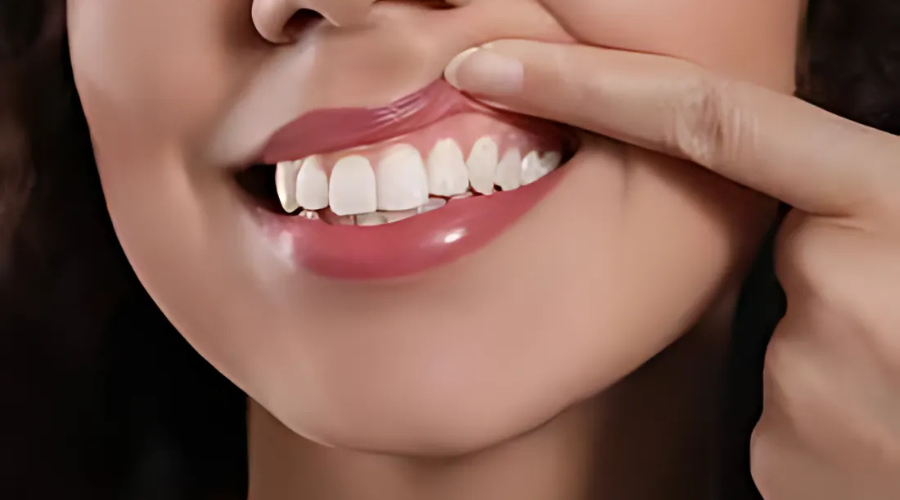

After surgery, the gums need time to heal. The patient is given post-care instructions, including prescribed medications, special mouth rinses, and dietary recommendations to aid recovery. Over the following weeks, the gums regenerate, reattaching to the teeth and restoring a healthy, natural appearance. Regular follow-ups ensure proper healing and long-term success.